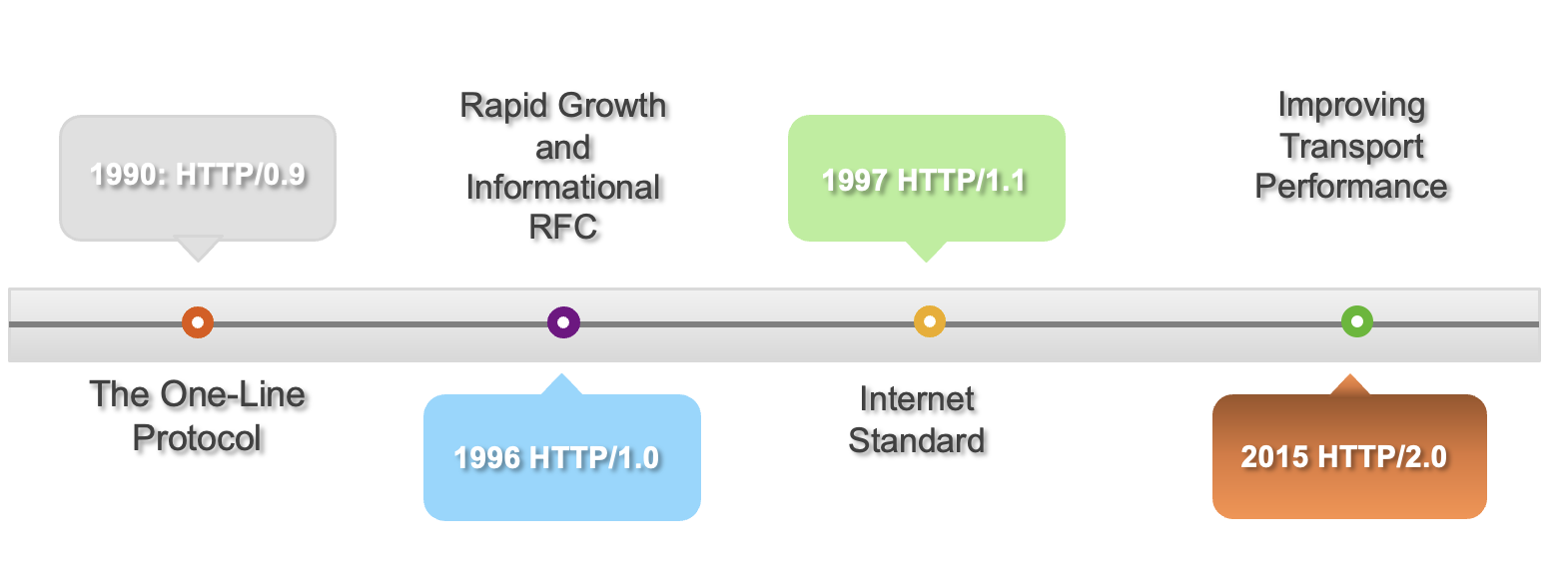
The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is the foundation of data communication on the web. Although HTTP/1.1 has been a standard since 1997, many web developers don’t fully utilize its advanced features for optimized performance. In this post, I’ll explain some key capabilities in HTTP 1.1 and how to leverage them.
HTTP History